Scientists have developed a groundbreaking new drug candidate that could revolutionize solid tumor treatments by selectively targeting tumor-associated macrophages that impede immunotherapy.
On Monday, the National Research Foundation of Korea announced that a collaborative research team led by Dr. Bae Hyun Soo and Dr. Kang Sung Ho from Kyung Hee University has created a peptide (amino acid mass) based drug candidate. This innovative treatment specifically targets and eliminates M2-type macrophages involved in tumor growth.
While cancer immunotherapy has shown remarkable success in treating blood cancers by activating immune cells to attack cancer cells, its effectiveness against solid tumors, such as lung cancer, has been limited. The complex tumor microenvironment in these cases often prevents drugs from penetrating effectively.
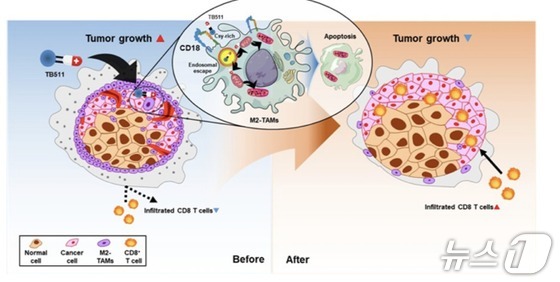
M2-type macrophages, known for their immunosuppressive properties, have long been recognized as a major obstacle to successful immunotherapy in solid tumors.
Drawing inspiration from nature, the research team developed a peptide-drug conjugate called TB511. This compound exploits the selective binding properties of natural toxins to the active CD18 protein found on M2-type macrophages while significantly reducing overall toxicity.
The newly developed drug demonstrates remarkable specificity, triggering cell death only in tumor-associated M2 macrophages without affecting normal macrophages. The treatment showed impressive results in animal testing, significantly inhibiting tumor growth across a range of solid cancers, including colorectal, lung, and pancreatic tumors.
Following recognition from South Korea’s Ministry of Food and Drug Safety for the precision of their approach this year, the research team is set to begin small-scale clinical trials.
Dr. Bae emphasized the drug’s potential: “Our treatment precisely eliminates cancer-promoting macrophages by targeting the CD18 protein, which is only activated within tumors. This breakthrough could pave the way for universal cancer immunotherapy drugs and advance precision immunotherapy techniques.”
The research team’s findings have been published in the premier cancer immunotherapy journal, The Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.
