
Nvidia’s TensorRT, newly designed for RTX Artificial Intelligence (AI) Personal Computers (PCs), now supports high-performance AI execution environments through Windows Machine Learning (ML)
At the Enterprise AI Solution Tour held on Thursday at the Grand Hilai Taipei in Taiwan, Kim Sun-wook, Senior Vice President of Technical Marketing at Nvidia Korea, announced that the integration of TensorRT and Windows ML has improved AI workload processing speed by over 50% compared to DirectML.

Kim explained that the TensorRT integration allows AI deployment on over 100 million RTX AI PCs with a package size eight times smaller than before, making it easier to start experiments with generative AI. The RTX-optimized TensorRT, announced at Microsoft Build, natively supports Windows ML, which runs on the ONNX runtime.
Kim emphasized that while TensorRT was originally built as a library for data centers, it has been completely redesigned for RTX AI PCs.
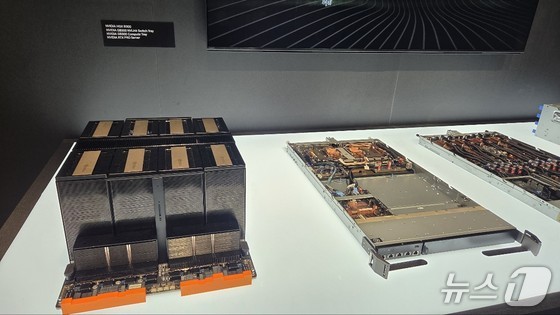
During the tour, Kim provided a detailed overview of the GB300 architecture, which combines the Blackwell graphic processing unit (GPU) and Grace central processing unit (CPU).
He explained that the GB300 computing tray allows for the configuration of multiple modules connecting Grace CPUs and Blackwell GPUs. NVLink, Nvidia’s core technology, manages GPU interconnections. Kim noted that NVLink 72 can connect 72 GPUs, and NVIDIA is developing technology to link 576 GPUs by combining four racks of 18 GPUs each.
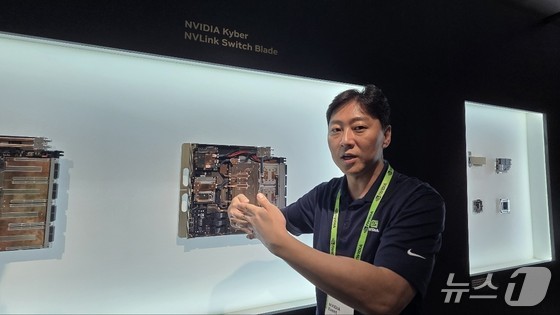
Kim described Kyber as the codename for Nvidia’s next-generation GPU project, which was designed to be much thinner and more efficient. It introduces a new approach to GPU configuration, moving away from traditional rack methods.
He also highlighted Nvidia’s Photonic technology, which saves energy by directly transmitting optical signals without electrical-to-optical conversion. This approach can save 80 watts per connection in data centers, significantly boosting overall energy efficiency.

Nvidia DGX Spark range on display on the 3rd floor of Grand Hilai Taipei, Taiwan. 2025.05.22 / News1
Kim also presented solutions for individual researchers, not just large-scale data centers.
He mentioned that solutions like DGX Spark and DGX Station enable researchers to work in their personal environments. By locally downloading and running models such as DeepSeek and Llama, they can operate large language models (LLMs) without relying on cloud services, resulting in cost savings.
NVIDIA offers Nvidia Inference Microservice (NIM), a set of accelerated inference microservices that allows companies to run AI models on Nvidia GPUs anywhere. This model is compatible with applications like AnythingLLM, Microsoft Visual Studio Code, and ComfyUI.




